The fundamental problem of our economy is that balance of payments crises and a perpetual risk of default have become the status quo.
This is because we import too much and export too little for the economy to be stable. Since FY04, our imports and exports have diverged so much that in FY22—during the run-up to the economic crisis—we imported 2.25 times what we exported, compared to 1.6 times in FY13 and 1.2 times in FY04 (Figure 1).

Instead of focusing on increasing exports and balancing our trade, we have relied on foreign remittances and external financing to fill the gap. Both increase the vulnerability of the economy to external shocks, and external financing comes with its own additional costs in the form of debt servicing and an implicit tradeoff on sovereignty when an economy inches closer to delinquency as Pakistan has.
Our policies continue to suppress exports while protecting unproductive domestically oriented industries to substitute imports—a strategy that has terribly failed in Pakistan and many other countries around the world.
Furthermore, uninformed rhetoric from various quarters of protected non-traded sectors and even some media outlets has not helped. For instance, a recent article in Business Recorder incorrectly claimed that “one of the members of the current interim setup who represents a specific sector tried to outsmart the system by using general non-export industries to cross-subsidize the export sector.” Even in other newspapers, claims regarding the export sector being provided with subsidies are frequent and have dangerously misguided the discourse on economic recovery and reforms. First, the authors of such misinformed propositions need to check their definitions of what a subsidy is. Second, they must present at least some evidence of where these subsidies are because our analysis indicates that there are none.
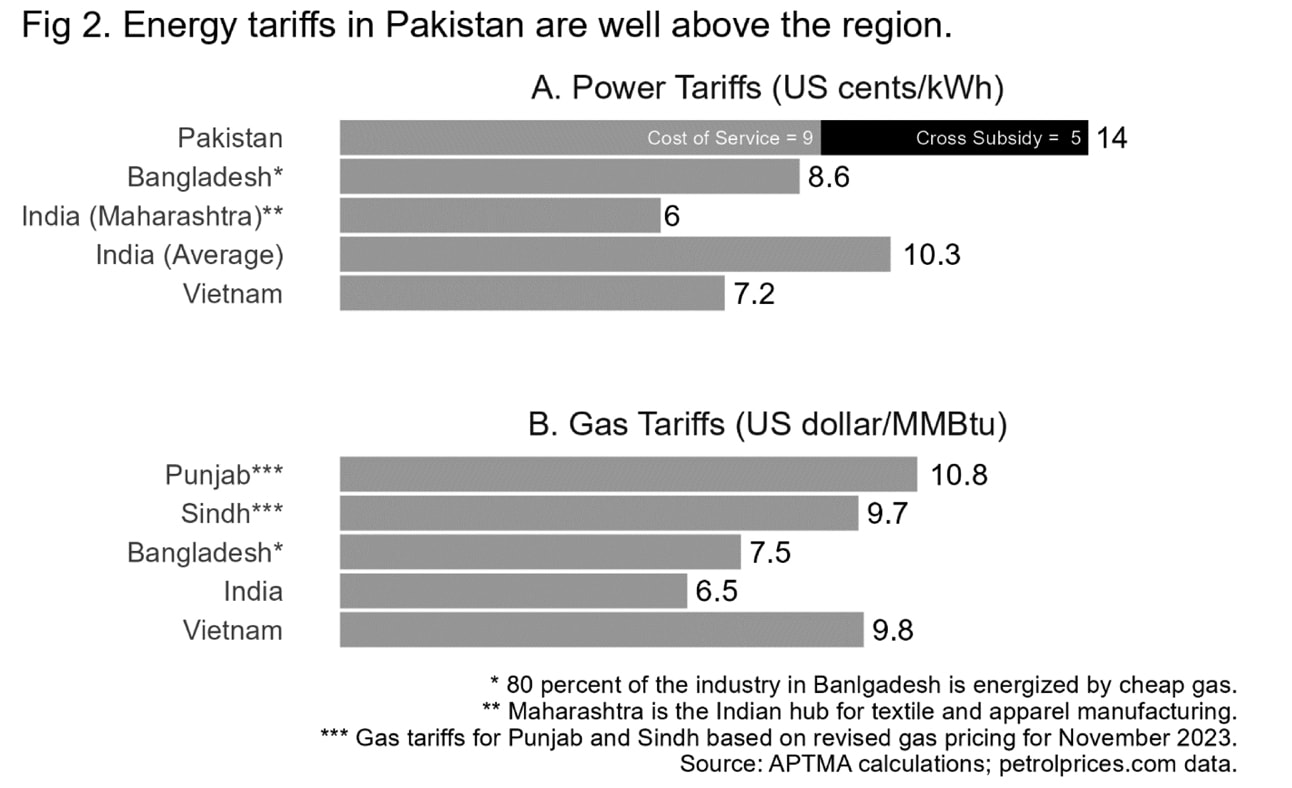
Power tariffs for exporters include a cross subsidy of around 5 cents/kWh to nonproductive sectors, making them almost twice the regional average. Similarly, gas prices following the recent reform have been increased to well above what prevails in the region, especially amongst competing economies (Figure 2).

Under the new pricing structure, the cost of captive power generation for export sectors has increased to as much as 15 cents/kWh for SNGPL and around 12 cents/kWh for SSGC consumers, which is around the same as getting electricity from the grid so that there is no real benefit in captive power generation. A statement from the IMF (International Monetary Fund) confirms that this was indeed the government’s purpose behind setting gas prices at these levels.
Ironically, captive power generation is—in the first place—incentivized by prohibitively high power tariffs that force productive sectors to pay for the government’s own social obligations and inefficiencies through cross subsidies, transmission and distribution losses, and stranded costs, etc.
The obvious balancing act was to remove the cross subsidy from power tariffs and equalize end-use prices for captive and grid electricity to shift industry away from captive generation. Instead, the government has included these unwarranted costs in gas prices to further undermine export competitiveness.
In the case of electricity—as acknowledged by the Power Division and power regulator NEPRA—a component of the cost of generation for power used by residential and agricultural consumers is extracted from industrial and commercial consumers, and this cross subsidy is clearly seen if one compares the power tariffs across different categories to the cost of generation and service (Figure 3).
But in the case of gas, it is a fuel delivered to consumers to convert and use as they prefer—i.e., as electricity in the case of industrial captive, and heat in the case of industrial process or household cooking and heating. Of the country’s total consumption, around 75 percent is indigenous gas, the cost of which, as per Ogra, is Rs 1,350/MMBtu, and 25 percent is imported LNG at approximately $13.50/MMBtu based on October 2023 rates. Accordingly, the weighted average cost of gas is around Rs 1,990/MMBtu.
Revised gas prices for export captive are Rs 3,145/MMBtu from March to November and Rs 3,830/MMBtu from December to March for SNGPL, and Rs 2,800/MMBtu throughout the year for SSGC consumers. Because prices for exporters are well above the cost, there is no subsidy to the export sector and, if anything, the export sector is again being made to subsidize the government’s debt and consumption in other sectors of the economy.
However, since we do not have enough indigenous gas to meet the entire country’s demand, the question of gas pricing is really one of resource allocation. By the law of price and demand, sectors that are subject to lower prices will consume more gas. So, do we want to allocate more gas towards productive uses, that will add value, earn foreign exchange, mobilize government revenue, stabilize the external sector, provide jobs, and create opportunities for productive investment that create future returns and benefit generations to come, or do we want to continue to burn away our precious resources in nonproductive activities?
The answer, based on prevailing policies, seems to be the latter. The energy sector provides vulnerable segments with cheap and underpriced electricity and gas but does so by systematically dismantling productive sectors that provide jobs to the same people, enabling them to purchase the same energy, efficient appliances and much more without any subsidies.
But this logic seems to completely escape the naysayers. Our policies continue to suppress exports while protecting unproductive non-traded sectors to substitute imports—a strategy that has terribly failed in Pakistan and many countries around the world.
The country’s international image and economic potential have deteriorated so severely that even strong and long-standing bilateral partners like Saudi Arabia and China have become wary of putting their money in Pakistan. For all our efforts to bring in foreign investment, nothing is materializing and how can it in a country where even domestic investors are increasingly parking their money in the safest and least productive of assets?
Pakistan’s gross external financing requirements, including current account deficits and amortization of debt, are, on average, projected at around $27 billion annually over the next 5 years. Prospects for receiving foreign investment remain bleak, and foreign investment in non-export sectors that do not generate returns in foreign currency is a liability in any case.
This is where we stand now: The foreign exchange shortage continues to persist, and exports for FY24 are likely to remain well below the FY22 peak of $32 billion. Following a brief appreciation, the exchange rate is depreciating again, which, coupled with the increase in gas prices, could very well reverse the downward trajectory of inflation, and result in a prolonged period of high interest rates. All of this will continue to cripple real economic growth and diminish the chances of recovery.
To come out of this vicious cycle of crisis after crisis and achieve sustained economic growth, a fundamental strategy of fostering competition and increasing exports must be adopted at all policy levels, across all sectors of the economy. Exports are competitive only if export sector input costs are at par with competing economies. Any form of taxation, either direct like sales tax or indirect like cross-subsidies, cannot be exported. The choice is simple: Export or perish.
Copyright Business Recorder, 2023
PUBLIC SECTOR EXPERIENCE: He has served as Member Energy of the Planning Commission of Pakistan & has also been an advisor at: Ministry of Finance Ministry of Petroleum Ministry of Water & Power
PRIVATE SECTOR EXPERIENCE: He has held senior management positions with various energy sector entities and has worked with the World Bank, USAID and DFID since 1988. Mr. Shahid Sattar joined All Pakistan Textile Mills Association in 2017 and holds the office of Executive Director and Secretary General of APTMA.
He has many international publications and has been regularly writing articles in Pakistani newspapers on the industry and economic issues which can be viewed in Articles & Blogs Section of this website.
























Comments
Comments are closed.