Scientists find way to create more breathable 3D-printed human tissues
3D-printing is growing each day with researchers discovering more ways to use it for various things. This time scientists have figured out a way to 3D-print more breathable tissues.
Researchers at Pennsylvania State University have taken a step forward in making lab-made tissues such as bones and cartilages become a reality. They have created a method of fabricating porous tissues, in which micro-pores allow nutrients and oxygen to circulate, and thus keeping the cells healthy.
This method requires taking human stem cells from human fat and then mixing them with a sodium alginate material found in seaweed. This can then be printed into particles that, once dissolved, leave small breathable pores in the fabric of the tissue, explained Digital Trends.
Experts want to 3D-print skin, bones and other body parts to help astronauts
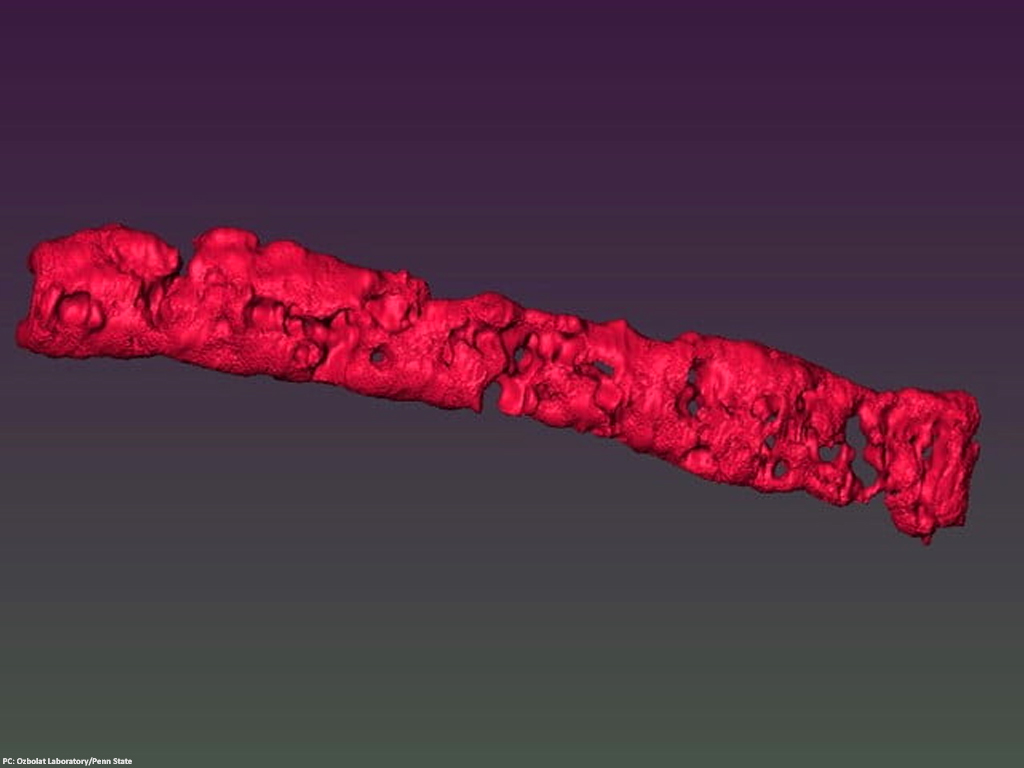
Such porous structures allow both nutrients and other fluids to circulate and demonstrate the potential for lab-grown tissue containing blood vessels. With the help of the stem cells mixture, the researchers 3D-printed strands of undifferentiated tissue which then is combined to form patches of tissue. The tissue was then exposed to a chemical solution that converts stem cells into specific cells like bone or cartilage.
“These patches can be implanted in bone or cartilage, depending on which cells they are,” said researcher Ibrahim Ozbolat. “They can be used for osteoarthritis, patches for plastic surgery such as the cartilage in the nasal septum, knee restoration, and other bone or cartilage defects.”
According to Eurek Alert, the researchers reported that the strands maintained 25% porosity and have pore connectivity of 85% for at least three weeks. However, at present only tiny patches can be made, which are easier to fabricate than growing artificial tissue on scaffolding.
However, there is still more work to be done on the technique. The team is further looking to use the same technique to create muscle, fat, and also an assortment of other tissues.
























Comments
Comments are closed.